Diagnosis of osteochondrosis dissecans, but what now? Klaus Pastl, OCD specialist from Linz, answers this and many other questions about osteochondrosis dissecans (OCD) in this guidebook. He talks about the symptoms, causes and various treatment options for osteochondrosis dissecans. He explains a wide variety of conservative treatment options as well as surgical materials and surgical methods. Among other things, he also talks about Shark Screw®, a screw made from human bone that is colonized by the body’s own cells and can help heal osteochondrosis.
Reading time: 3 min
Author of the article: Dr. Klaus Pastl
Foot surgeon and OD expert from Linz, Austria
The author is a renowned specialist in Austria for foot surgery and osteochondrosis dissecans surgery.
Updated 15.09.2022
What is osteochondrosis dissecans, or OCD for short?
Osteochondrosis dissecans, also called OCD, is a disease that leads to cartilage and bone damage (bone necrosis). More precisely, it leads to the death of bone close to the joint. At the beginning of this disease, only the bone is affected (stage I-II), the cartilage remains intact. As the disease progresses, the cartilage in the joint changes (stage II-III), until finally the cartilage or bone becomes detached (stage III-IV). The cartilage bone fragment that detaches at an advanced stage is also called a joint mouse or dissekat. It can move freely in the joint space, which can lead to considerable pain but also damage and blockage of the joint. If these osteochondral defects remain untreated, the joint can be partially destroyed. As a later consequence, joint wear and tear, i.e. osteoarthritis, may develop. Osteochondrosis dissecans occurs most frequently in the knee joint, but can also occur in the hip, elbow joint or ankle joint (talus). Mainly affected by OCD are young people who are growing and athletic people. However, older people can also suffer from osteochondrosis dissecans. Often the course of the disease shows considerable differences between young and old affected persons.
Therefore, osteochondrosis dissecans is also divided into 2 groups:
Juvenile OCD (JOCD): In children as well as adolescents with an open growth plate.
Adult OCD: In adults with a closed growth plate.
What are causes of osteochondrosis dissecans?
The exact causes that trigger osteochondrosis dissecans have not been fully clarified to date. It is assumed that there is a local reduction in blood flow to the affected bone area. Of course, there are also other factors that favor the development of osteochondrosis dissecans. For example, children and adolescents who are active in sports are more likely to develop osteochondrosis dissecans. Therefore, it is assumed that recurring mechanical loads during sports trigger a reduced perfusion of the bones, which leads to the death of small bone areas (necrosis).
Such constant loads, e.g. in the knee joint, can cause microtrauma, which leads to the local blood supply at the joint being disturbed. Such microtrauma is mainly caused by sports that require rapid stopping movements or changes of direction, as is the case with soccer or tennis players.
Osteochondrosis dissecans and flake fracture - the differences
If osteochondrosis dissecans is a cartilage bone fragment that dies (becomes necrotic), a flake fracture is a piece of cartilage bone (osteochondral defect) in the joint that breaks out of the joint due to force. Treatment for both types of disease is surgery and refixation of the free joint body (flake – fracture or articular mouse) with screws made of human bone to the vital bone.
What symptoms can occur?
Often, at the beginning of the disease, there are no symptoms and the affected person is symptom-free. OCD may not be recognized, especially in the early stages, and thus is often discovered only by chance during an X-ray or MRI. Initial symptoms may include pain in the respective affected regions. If the disease progresses and thus detachment of the bone fragment occurs, the pain becomes significantly more severe. It can also lead to joint swelling and inflammation of the damaged regions. In the worst case, joint locking occurs. In affected individuals, the affected joint suddenly jams, which in turn can trigger severe pain. The gait pattern can also change as a result.
How can osteochondrosis dissecans be treated?
How OCD is best treated depends on each patient and the particular stage of osteochondrosis dissecans. Treatment is divided into conservative and surgical therapy. It also depends on which area is affected and how old the patient is.
The four stages of osteochondrosis dissecans
Osteochondrosis dissecans can be divided into 4 stages. Depending on the stage, the therapy can also be derived.
- Stage 1: softened but intact cartilage, stable lesion.
Optional therapy: Regular check-up of the joint in order not to miss a progression of the disease. Unloading of the affected joint. At this stage, osteochondrosis dissecans may partially regress.
- Stage 2: partial cartilage discontinuity, stable lesion.
Optional therapy: regular control of the joint. To stimulate blood flow to the dissect, surgery may be helpful.
- Stage 3: not yet dislocated, complete dissecat.
Optional therapy: Surgery may be helpful to stimulate blood flow to the dissected joint. In this case, screws made of human bone have proven effective for stabilization and revascularization (blood flow / sprouting of small vessels) of the dissecat.
- Stage 4: free or detached dissecting catheter
Optional therapy: In order to stimulate blood flow to the dissect, surgery may be helpful. In this case, screws made of human bone have proven effective for stabilization and revascularization (blood flow / sprouting of small vessels) of the dissect.
Are you looking for an osteochondrosis dissecans expert or would you like to get a second opinion? We will be happy to help you without obligation!
Conservative treatment options for OCD
Conservative treatment is only applicable in stage 1. In this case, the respective affected joint is spared or relieved for a longer period of time. This leads to an improvement in blood circulation and a reduction in the pressure load on the affected joint. Sports with many jerky movements as well as jumping and landing movements, such as tennis or soccer, should not be performed during this period. In addition, anti-inflammatory medication can be taken if necessary. Once the patient is no longer in pain, everyday activities can be resumed. Sports should not be resumed until an improvement in the findings has been confirmed by an MRI and the patient no longer feels any pain.
Surgical treatment options OCD
If conservative therapies do not achieve satisfactory results, surgery is recommended, depending on the stage. Do you have osteochondrosis dissecans and are looking for a specialist who can find the optimal treatment option for you? Contact us and we will recommend an expert in your area without obligation!
What surgical techniques can be performed?
There are now many different surgical techniques that can be performed for osteochondrosis dissecans. The following are listed here:
- Refixation of the OCD fragment with screws from human bone.
- Osteochondral allograft transplantation
- Bone cartilage transplantation
Which surgical materials can be used?
If the cartilage bone dissect needs to be refixed during surgery, screws made of human bone (Shark Screw®) are the means of choice for fixation. These support the fragment during revascularization, are remodeled into the patient’s own bone, and spare each patient the second operation, metal removal.1
Can the Shark Screw help with osteochondrosis dissecans?
“Since Shark Screw®, a screw made from human bone, is colonized by the body’s own cells after insertion, it is optimally integrated into the natural bone remodeling process,” says Dr. Klaus Pastl. This is made possible by the so-called Havers channels inside the screw. Bone cells and the body’s own vessels can settle in these channels and thus expand. This helps to supply the bone fragment with nutrients again. In this way, the dead bone fragment regains contact with vital patient bone. In addition, the Shark Screw® saves the patient a second operation to remove the metal, but also reduces sick leave and risks.
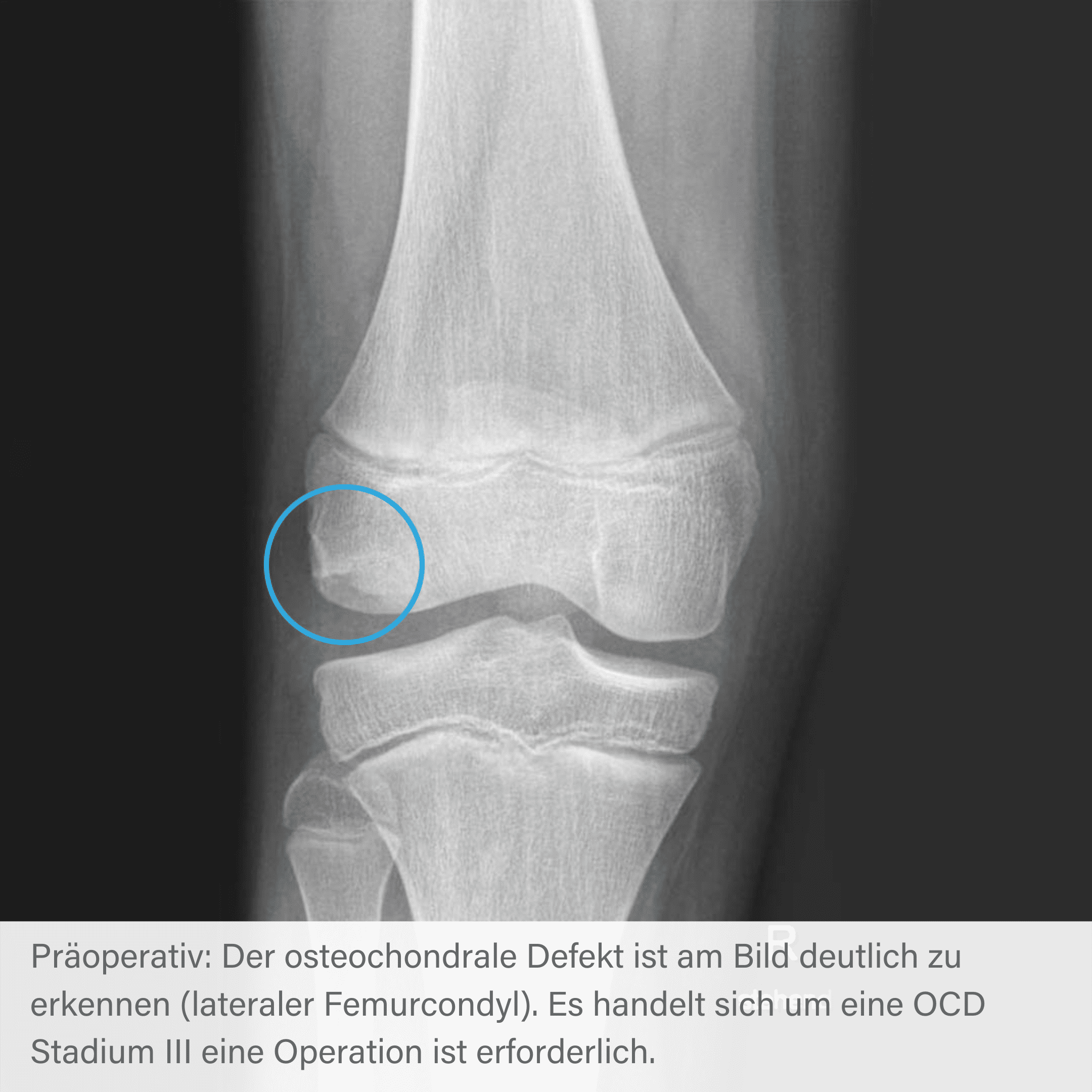
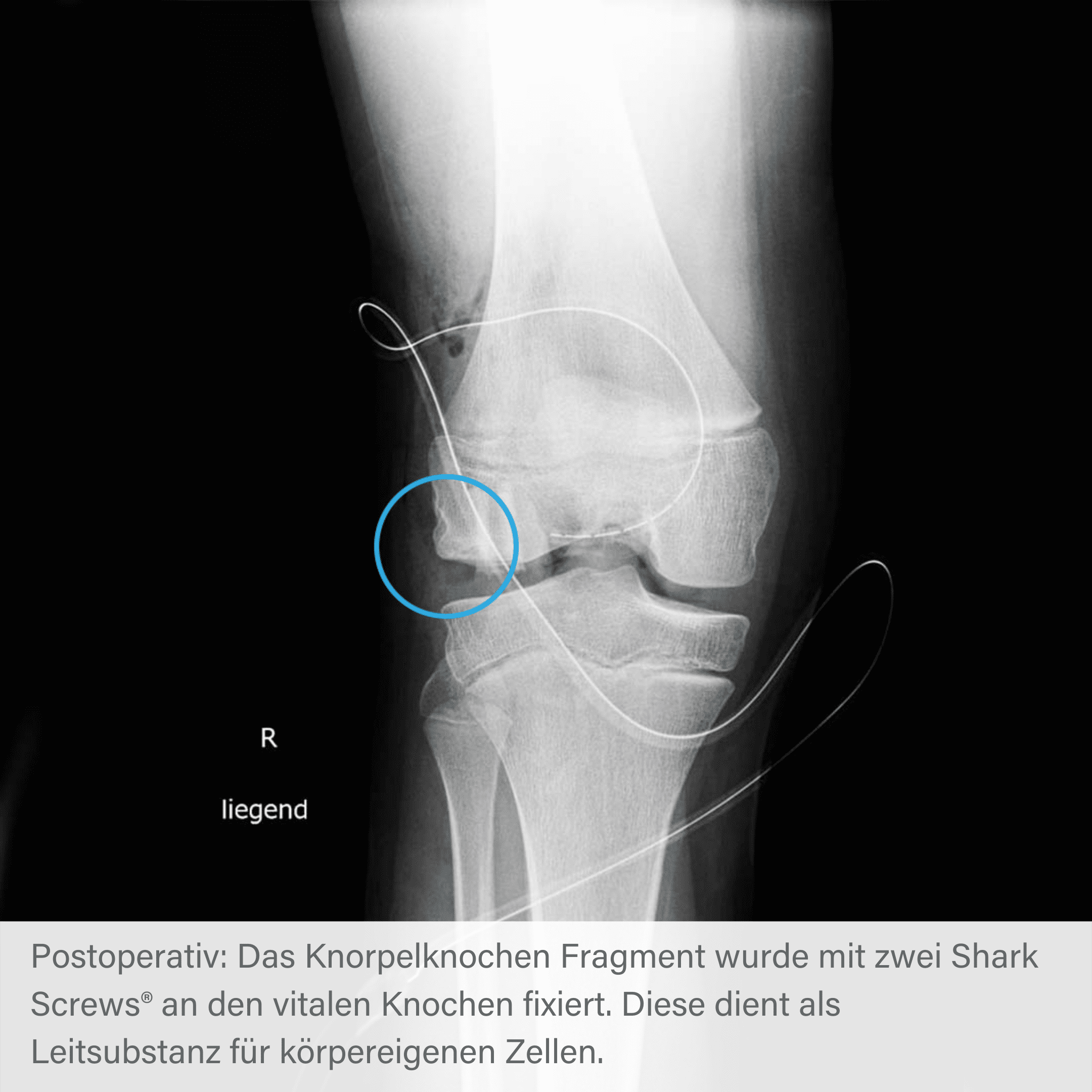
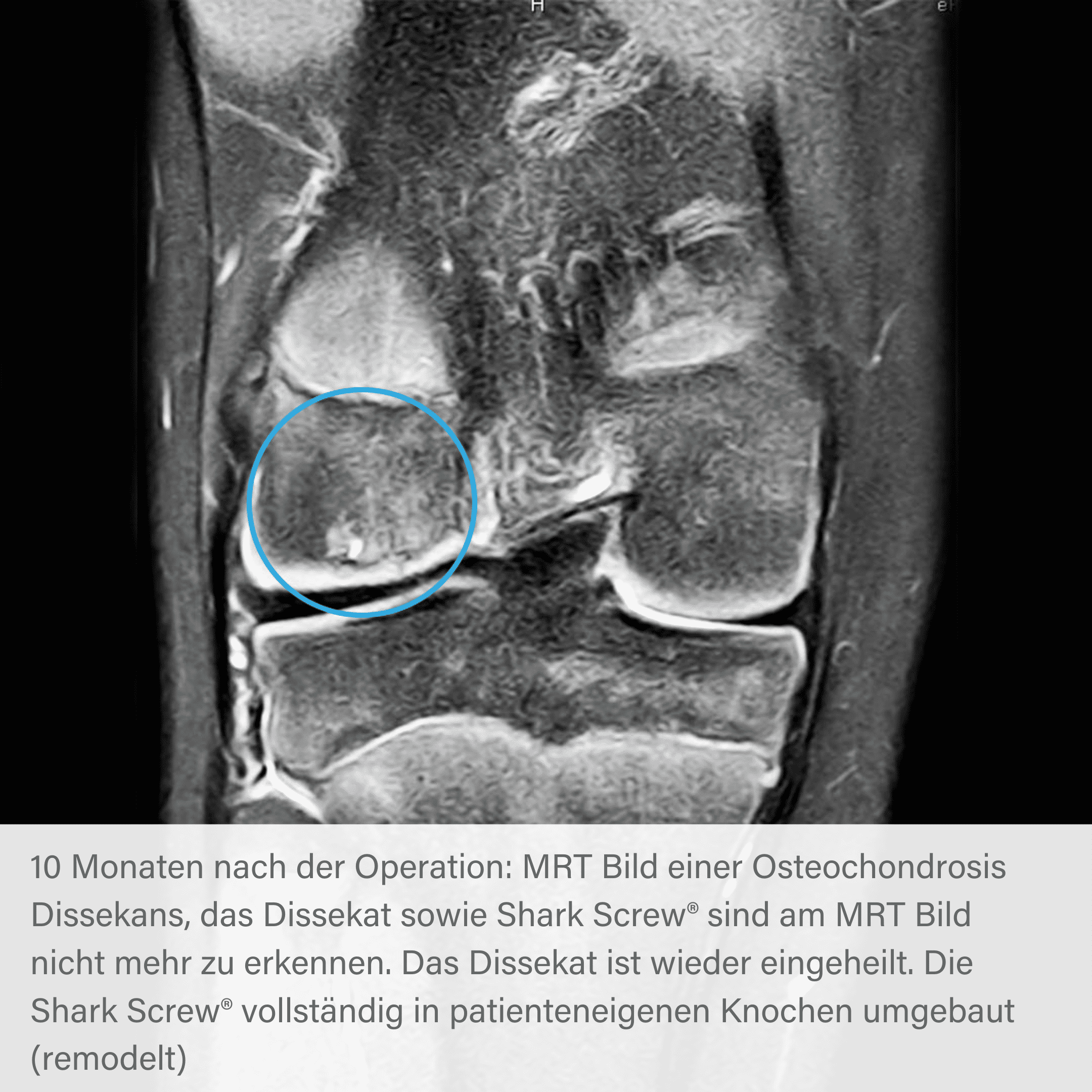
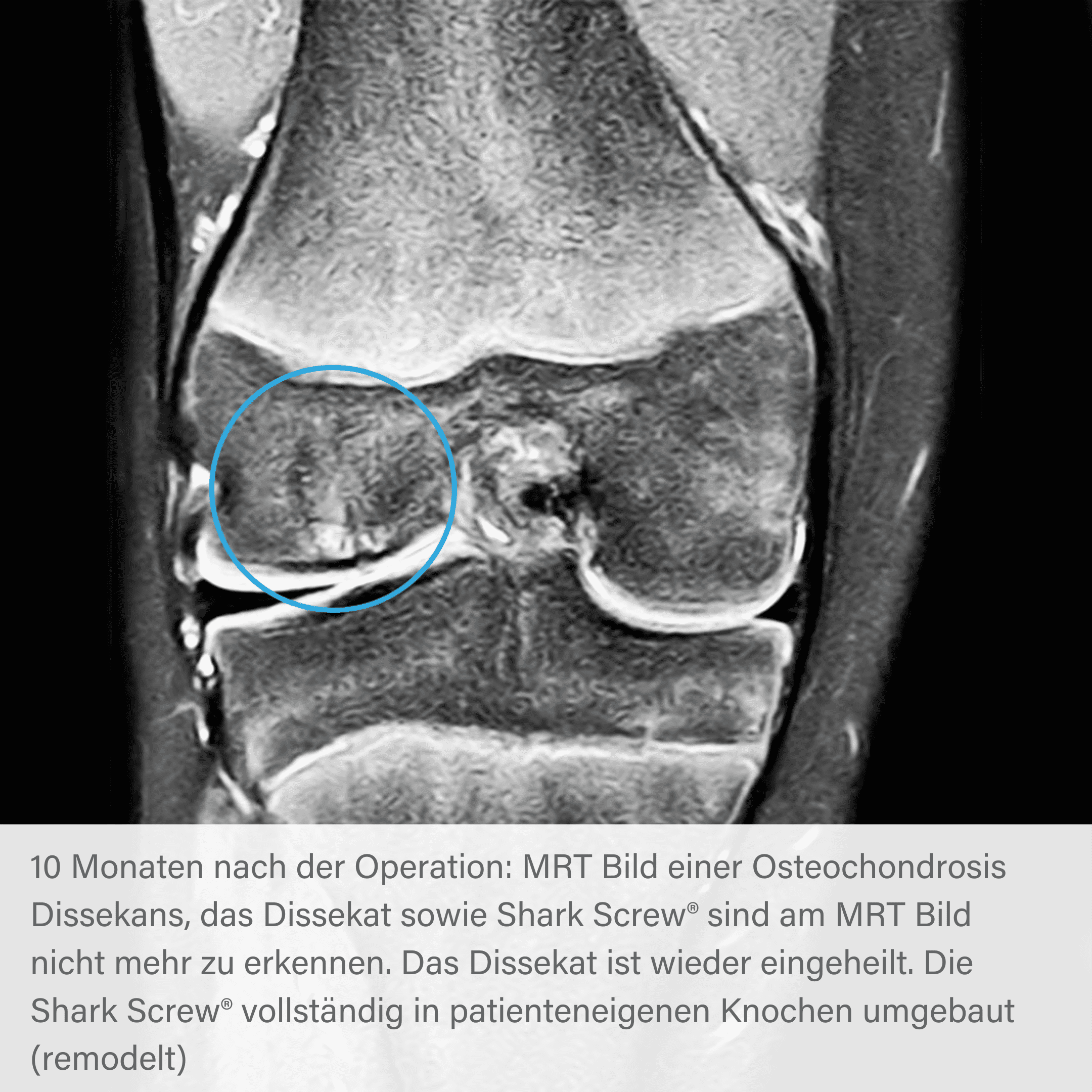
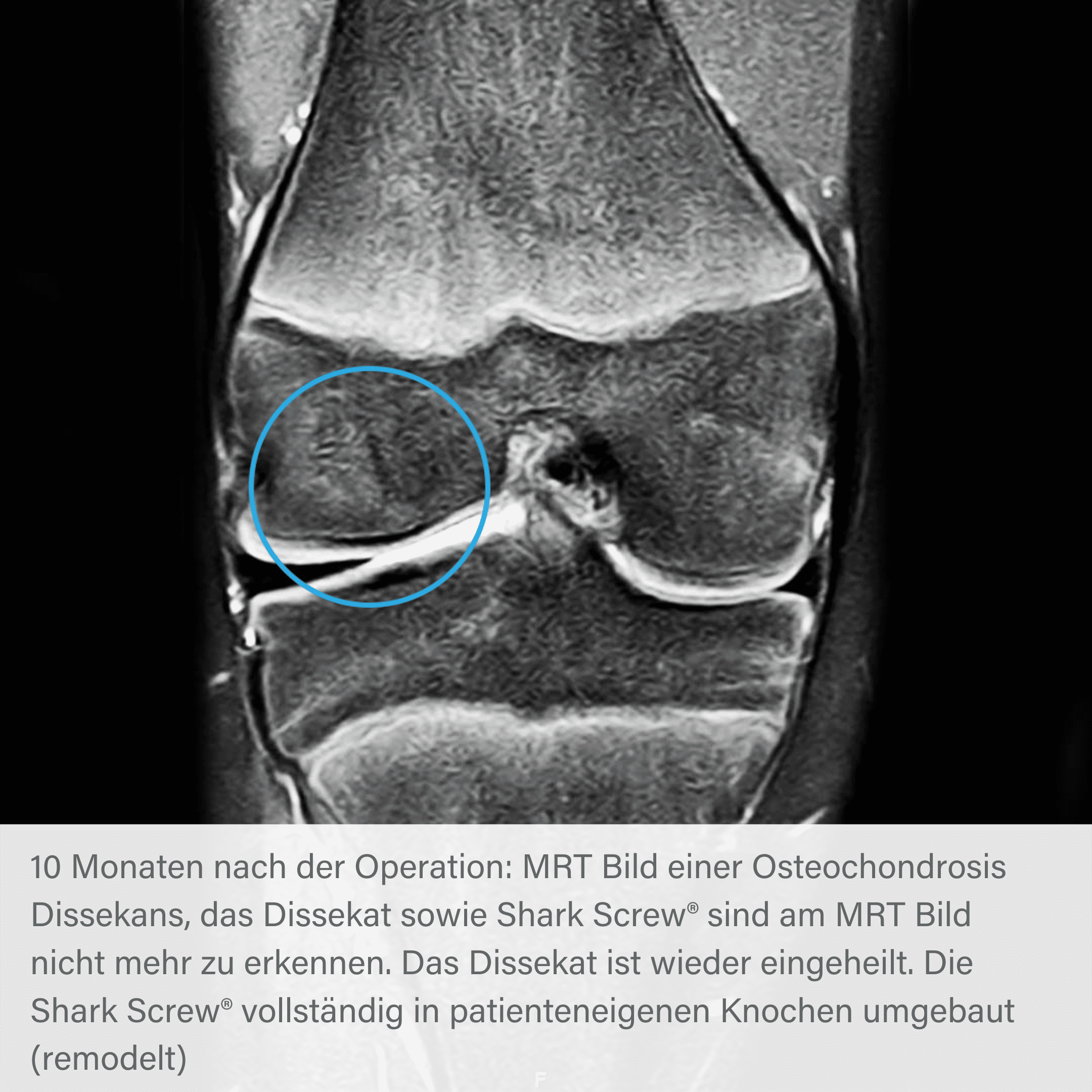
Radiographic course of osteochondrosis with Shark Screw®.
Are you looking for an expert to provide you with the screw made of human bone, the Shark Screw®? We will be happy to recommend an expert to you.
What is the follow-up treatment for osteochondrosis dissecans?
After the operation, the joint must be relieved for several weeks. Appropriate gymnastics and lymph drainage can reduce any swelling that occurs. The course of the operation is checked by MRI at regular intervals. Patients often ask the question: When can osteochondrosis dissecans patients return to sports? No concrete statement is possible here. When sport can be practiced again depends on the stage of the OCD and the course of recovery. A consultation with the treating physician should always take place beforehand. If sports can be resumed, it is recommended to start with sports that are easy on the joints, such as swimming or cycling.