An ankle fracture is the fracture of one or even more bones of the ankle joint (tibia, fibula & talus). There are 2 types of fractures to distinguish: A simple fracture, where you can still walk in the best case, or multiple fractures of the ankle joint, where the movement of the ankle joint is restricted for a long time.
In this guide, Dr. Boris Tirala, ankle fracture expert from Schwaz in Tyrol, talks about noticeable symptoms of an ankle fracture & how best to treat a broken ankle.
“Before an surgery, patients should definitely seek detailed advice and comprehensive information on the clinical picture. Often a second opinion can also be useful,” says Dr. Boris Tirala.
Reading time: 6 min
Author of the article:FA Dr. Boris Tirala
Specialist for Orthopedics & Trauma Surgery
Updated 22.02.2023
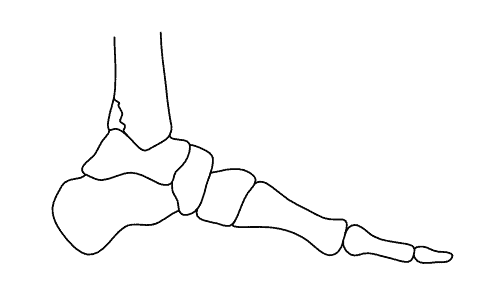
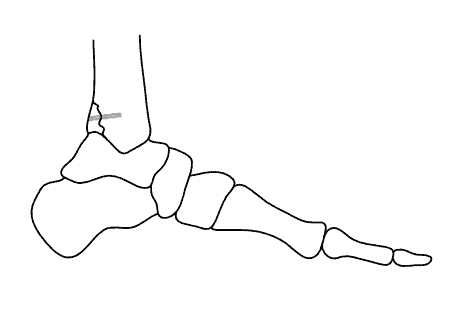
Ankle fracture / The anatomy of the ankle joint
Basically, the ankle joint consists of 3 bones: Tibia (shin bone), Fibula & Talus (ankle bone).
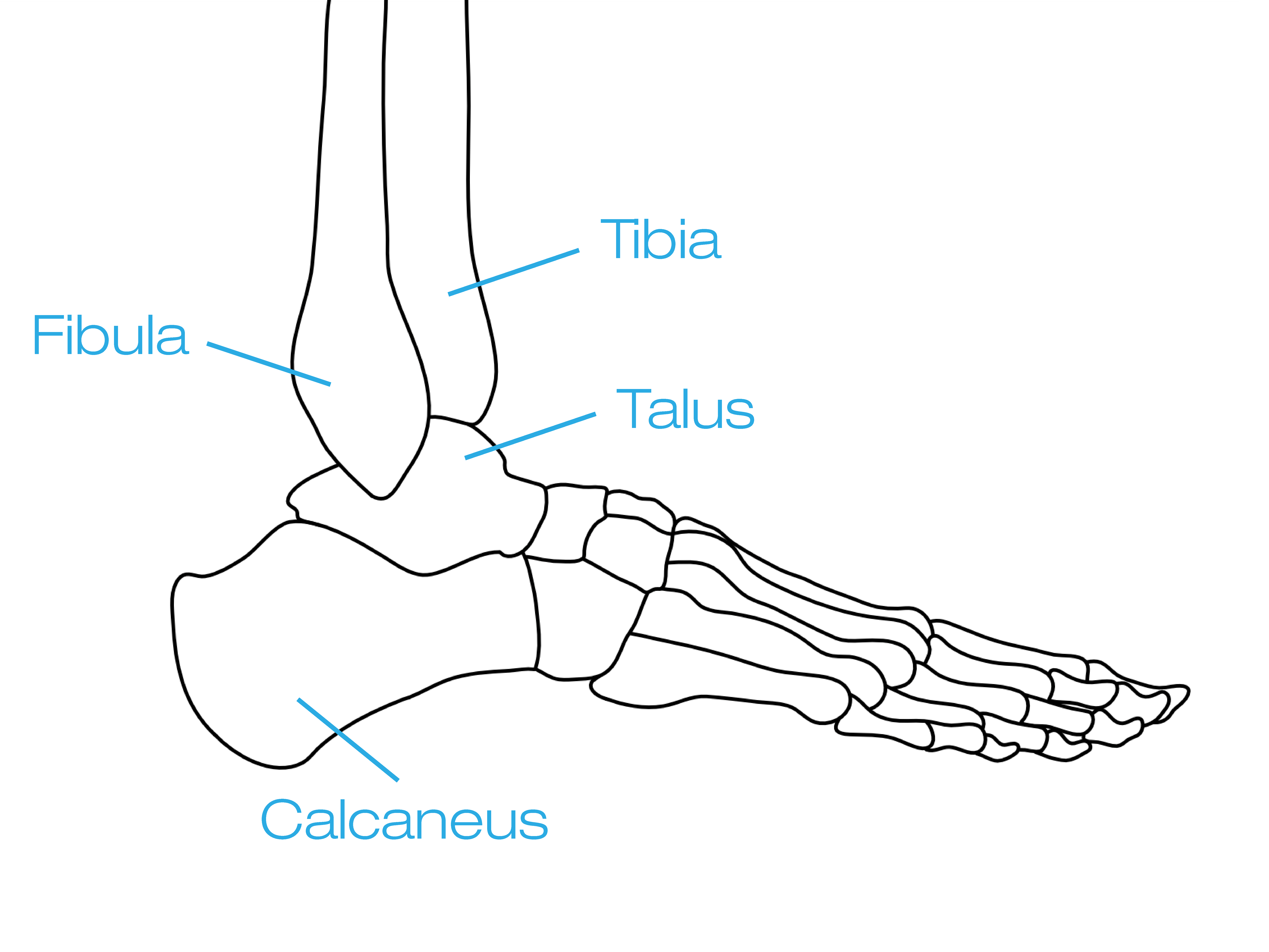
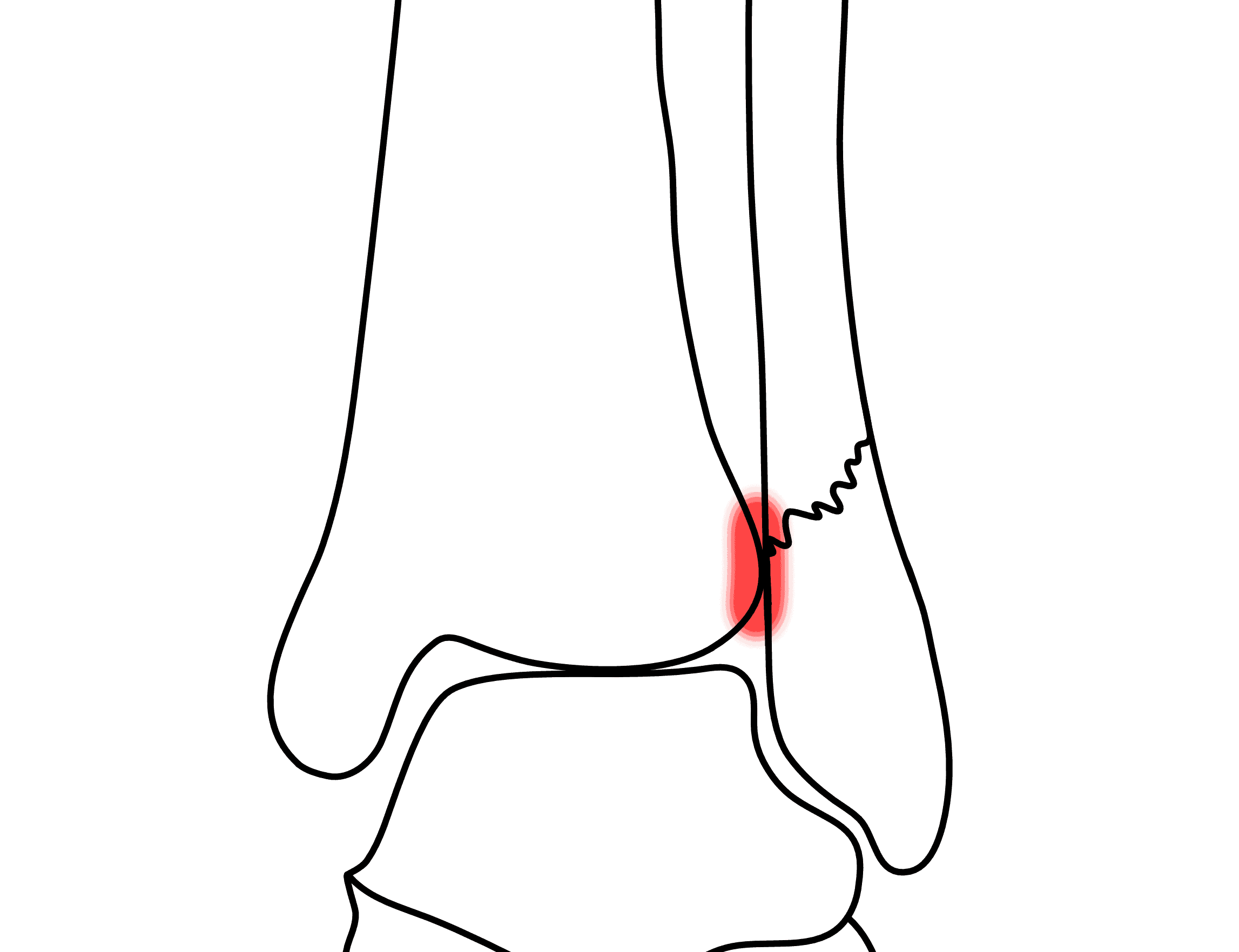
The tibia & fibula have special bony structures that together form the ankle joint. First, there is the medial malleolus. It is a small protruding bone located on the inside of the ankle at the end of the tibia. In addition, there is the posterior malleolus, which forms the back of the tibia, and the lateral malleolus, which is located at the end of the fibula on the outside of the ankle.
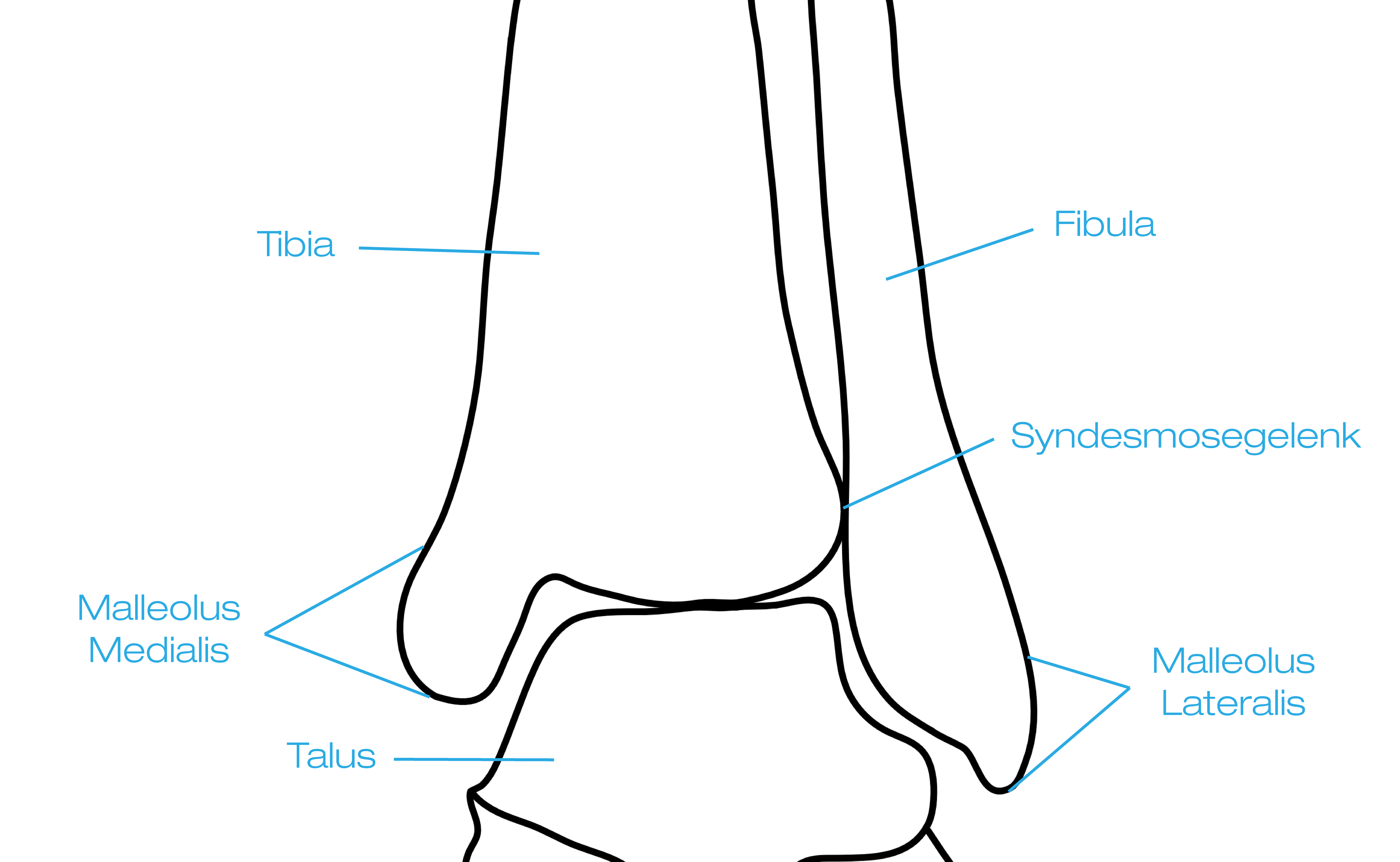
Doctors classify ankle fractures by the area of the broken bone. For example, if the end of the fibula is broken, it is called a lateral malleolus fracture. If both the tibia and fibula are fractured, it is called a bimalleolar fracture. More on this below.
Field reports ankle fracture
The decision which treatment is necessary for you should always be clarified with an expert. But what was the experience of other people with ankle fracture? In the following video series, patients talk about personal experiences with ankle fractures.
Classification of ankle fracture
If a fracture of the ankle joint occurs, it is classified according to how much the individual bone fragments have shifted from their original position.
- Open fracture
If the ankle joint breaks and bone fragments shift through the skin, this is called an open fracture. This is an emergency, so the fracture should be treated as soon as possible, because there is a risk of dirt and foreign bodies entering the open wound, which increases the risk of infection. - Displaced fractures
Bei einer verschobenen Sprunggelenksfraktur sind ein oder mehrere Knochen im Sprunggelenk gebrochen und verschoben. This type of fracture also requires surgical treatment. - Non-displaced fractures
Non-displaced fractures do not require urgent surgical treatment because the bone fragments are separated but still in the original position.
Classification according to Weber - A, B & C
In the case of a fracture of the ankle joint, the Weber qualification is often used. Bernhard Georg Weber was a Swiss surgeon who dealt predominantly with fractures as well as pseudarthroses, thus giving his name to the Weber ankle fracture classification. The classification distinguishes between the different locations of the fracture as well as the number of broken bones.
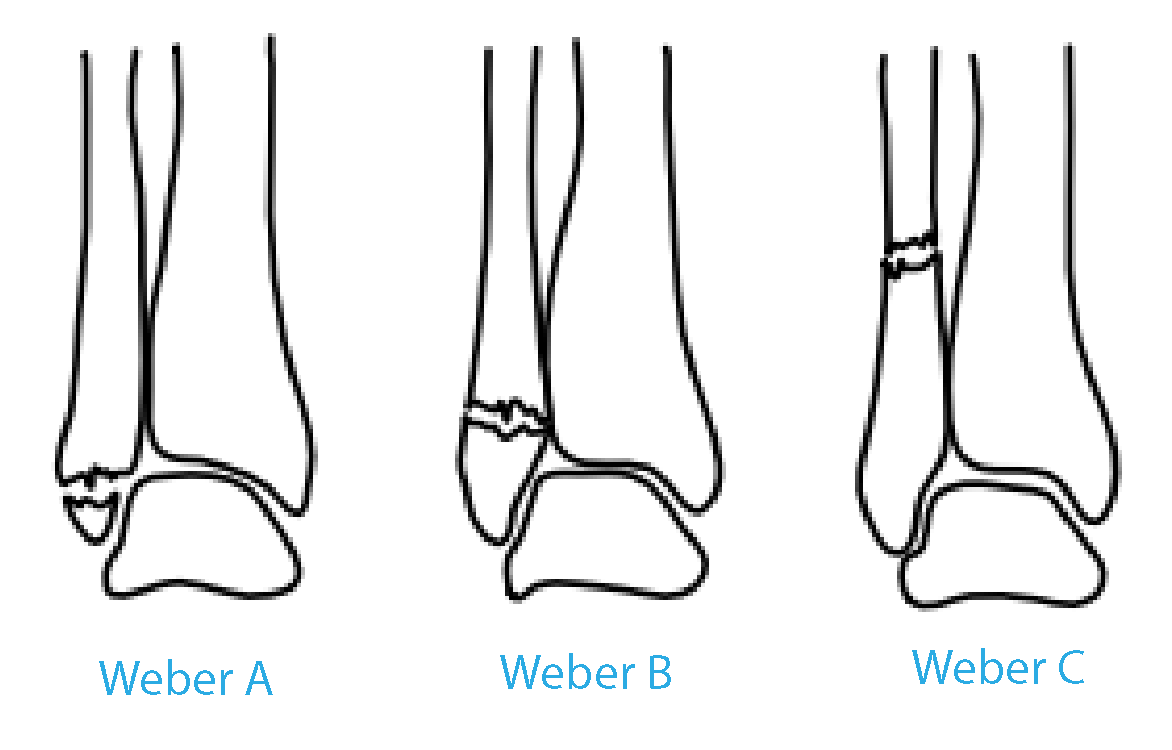
Weber A Fracture
In the Weber A fracture, the fracture gap is below the syndesmosis (ligamentous structure), which means that the syndesmosis is intact, i.e. the ligamentous structure is not torn.
Weber B Fracture
In the Weber B fracture, the fracture of the fibula is at the level of the syndesmosis (ligamentous structure). Possible lesions of the syndesmosis may occur.
Weber C Fracture
In the Weber C fracture, the fracture of the fibula occurred over the syndesmosis (ligamentous structure). In this case, the syndesmosis and the membrane interossea (connective tissue layer) is ruptured (torn).
“The most common type of fracture is the Weber B fracture,” said expert Dr. Boris Tirala of Austria. In all types of fracture, it is also possible that the medial malleolus or medial ligament are also injured, but this is not a decisive point for classification according to Weber. A bimalleolar ankle fracture (bimalleolar OSG fracture) is when the outer ankle as well as the inner ankle are fractured. If the posterior inferior tibial edge is also affected, the fracture is referred to as a trimalleolar ankle fracture.
Do you have questions about the Weber fracture or do you want to be treated with Shark Screw® a screw made from human bone? Find Shark Screw® experts near you.
Causes of ankle fracture
The cause of an ankle fracture is usually an injury. The fracture of the ankle joint can be caused, for example, by twisting, tripping, turning or rolling the ankle or by a fall as well as an accident.
Symptoms of ankle fracture
There are some symptoms that indicate an ankle fracture. If acute, severe pain occurs as well as swelling in the area of the ankle, but also bruising indicates this. The affected person finds it difficult to put weight on the foot, and a feeling of numbness and coldness may also occur. If the ankle joint is also dislocated, a deformity is also evident.
Ankle fracture - the different types
Medial malleolus fracture / medial malleolus fracture
Die mediale Malleolusfraktur, oder auch Innenknöchelfraktur genannt, ist der Bruch des unteren Teils des Schienbeins. Often the fracture of the medial malleolus occurs in combination with other fractures of the ankle.
Conservative treatment
If the fracture is not displaced, the fracture may be immobilized with a walking boot or cast, with no weight bearing for several weeks. As a result, the bone usually heals without complications.
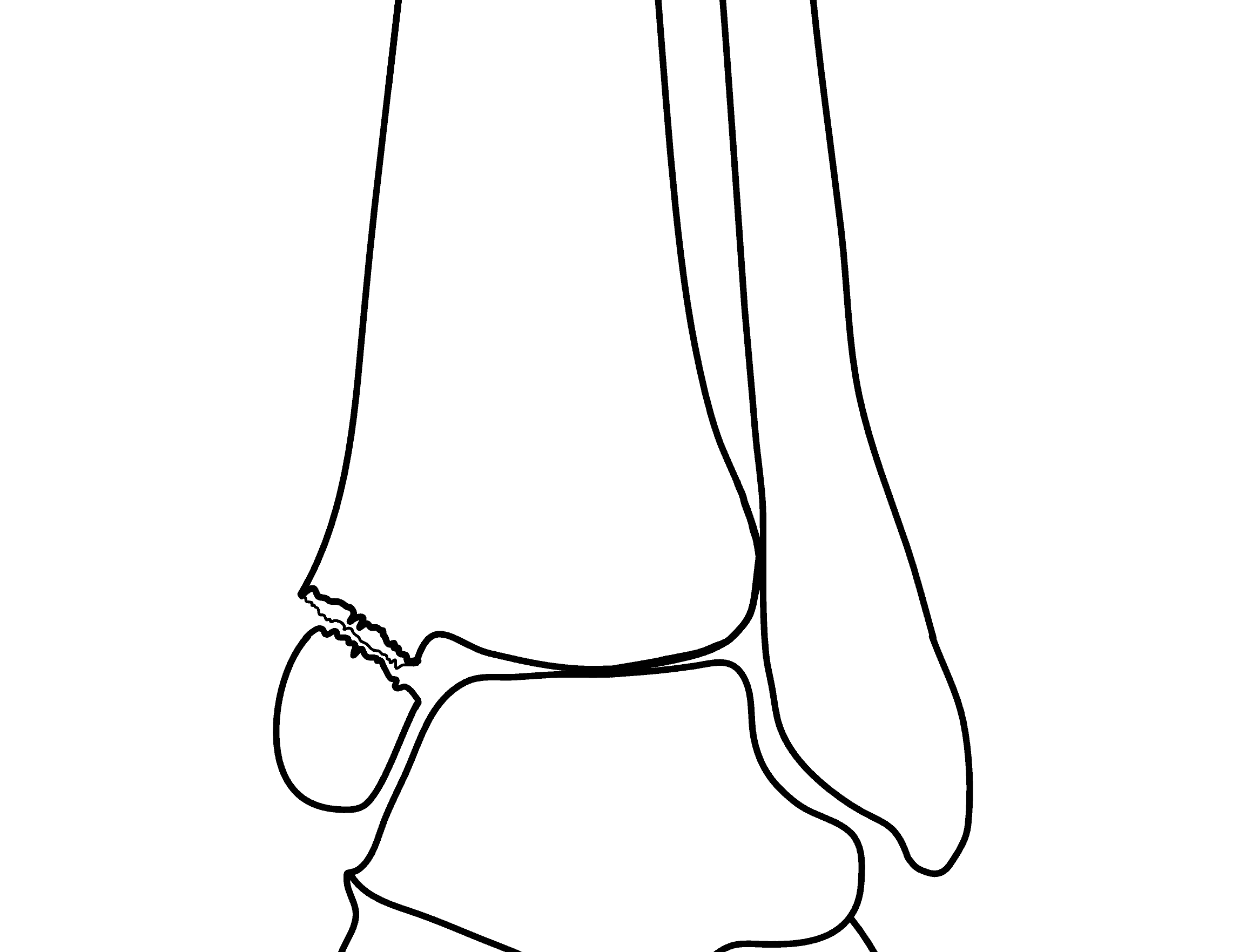
Surgical treatment
If the hernia is displaced, surgery is usually required. Depending on how much the fracture is displaced or how large the fracture is, different screws or plates are used, so-called osteosynthesis material. If the Shark Screw®, a screw made from human donor bone, is used in the surgical treatment, the patient is provided with 100% natural materials and is not exposed to the risk of a 2nd operation for metal removal.
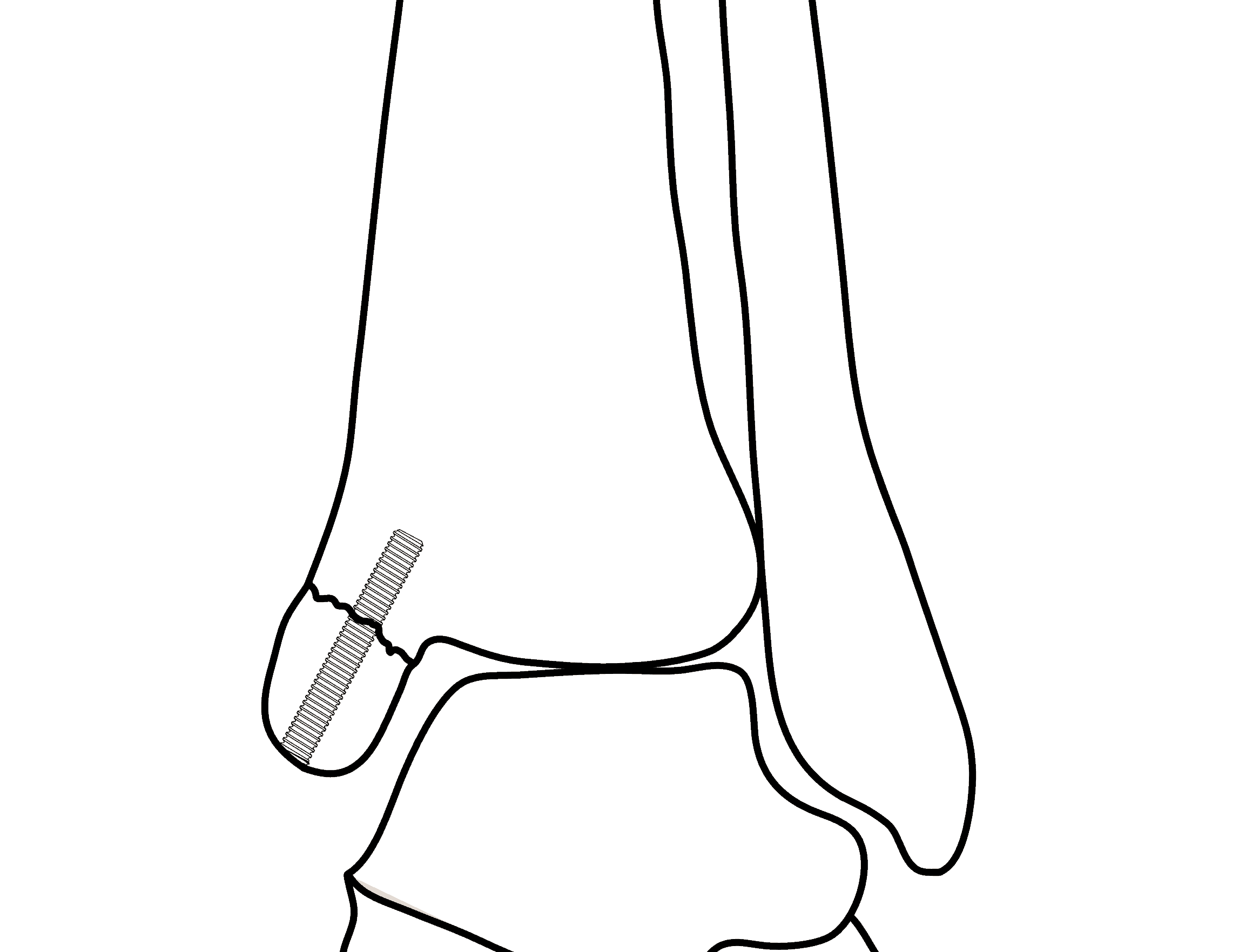
Malleolus Lateralis Fracture / External Ankle Fracture
Lateral malleolus fracture, also called lateral malleolus fracture, occurs when the lower fibula is fractured.
Conservative treatment
Similar to the medial malleolus fracture, the fracture can be immobilized with a walking boot or cast, provided the fracture is not displaced. In most cases, the foot can be weight-bearing in a walking boot or cast.
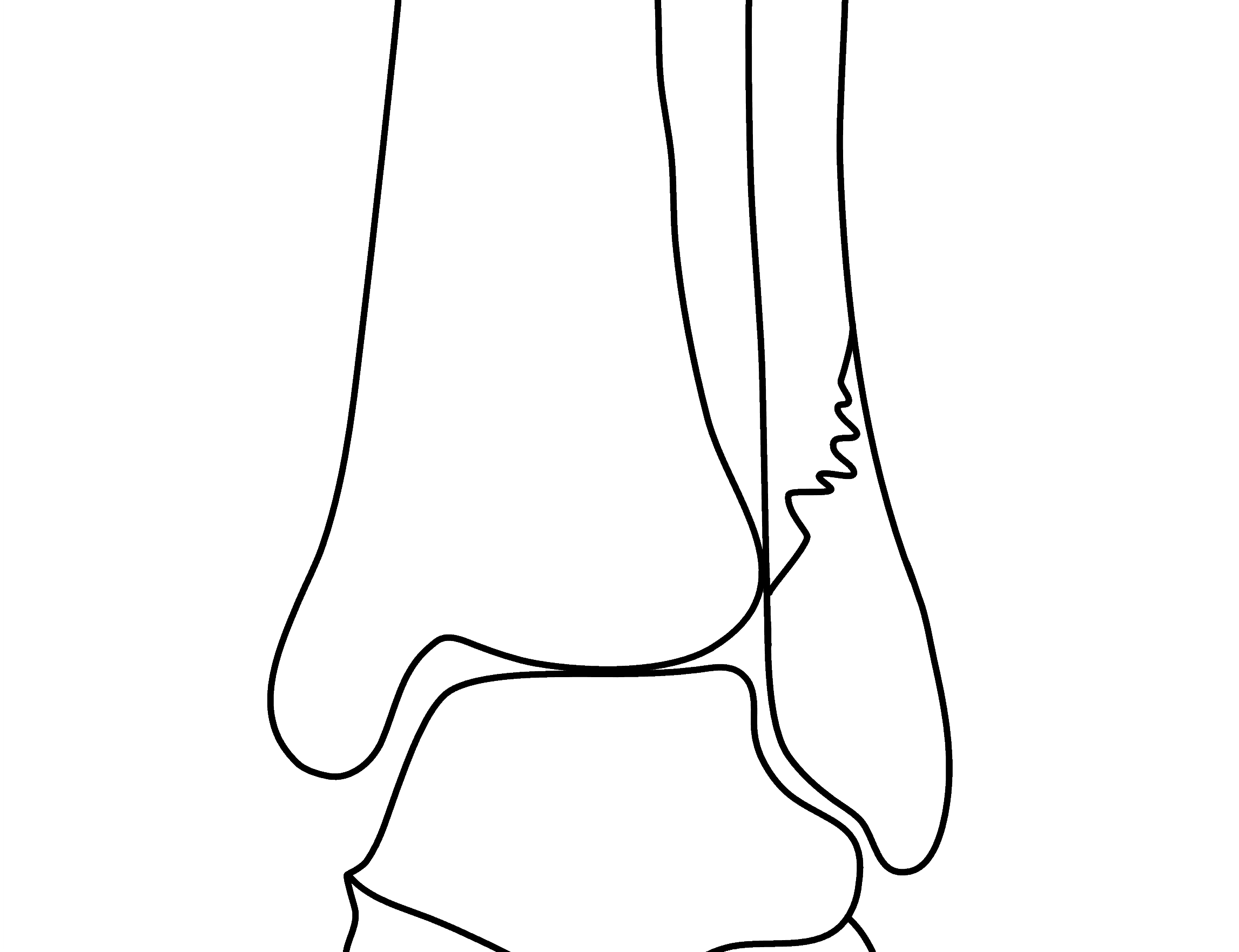
Surgical treatment
If the lateral malleolus fracture is displaced, surgery is necessary. Screws from human donor bones can be used for this purpose. This provides patients with a 100% natural restoration option entirely without metal.
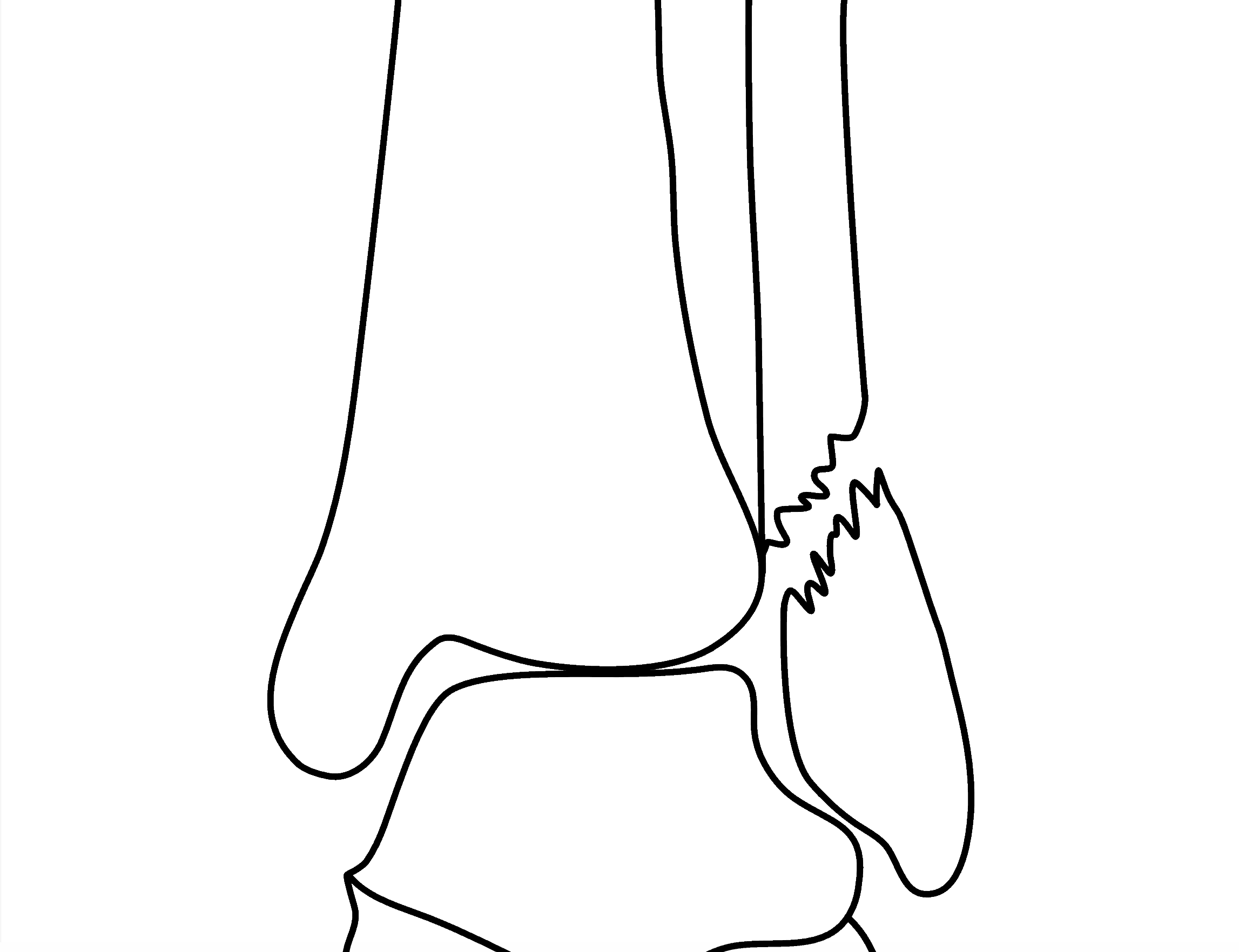
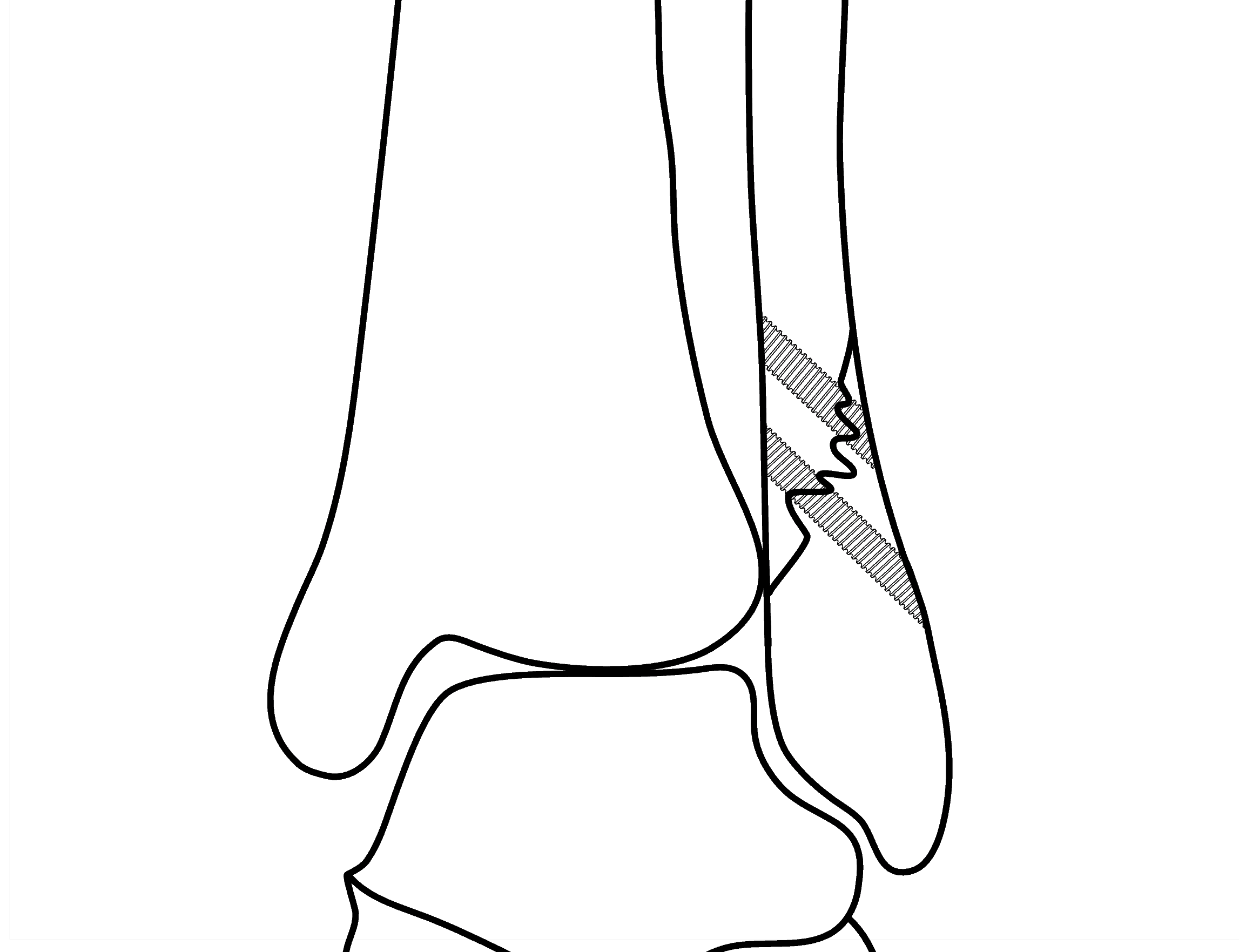
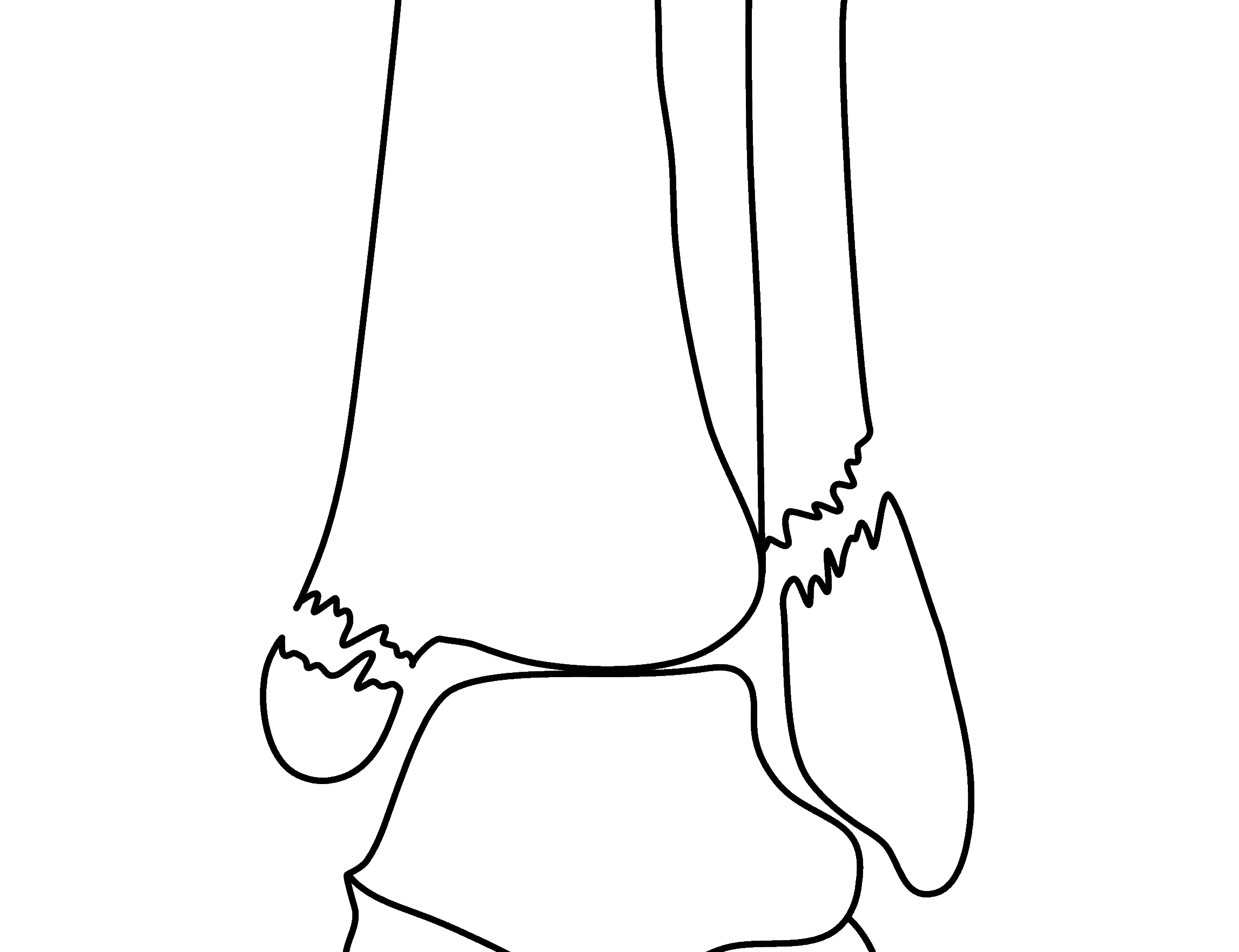
Malleolus posterior fracture / Volkmann triangle
Posterior malleolus fracture / Volkmann triangle This fracture most often occurs in conjunction with other fractures.
Conservative treatment
In most cases, a removable splint or cast can be worn to immobilize the foot. A non-displaced fracture is a prerequisite for this.
Surgical treatment
In case of large fractures, surgery is necessary. Various surgical materials can be used, including screws made from human bone. Learn more about Shark Screw® and human bone screws here.
Bimalleolar Fracture & Bimalleolar Equivalent Fracture
If the outer ankle and the inner ankle are fractured, this is called a bimalleolar fracture. The fracture is extremely unstable because both sides of the bone are injured.
Conservative treatment
If the bimalleolar fracture is reasonably stable, it can be immobilized with a cast.e. This will take a few weeks, and the foot must not be loaded under any circumstances.
Surgical treatment
In most cases, a bimalleolar fracture requires surgical treatment because both the medial and lateral malleoli are fractured.
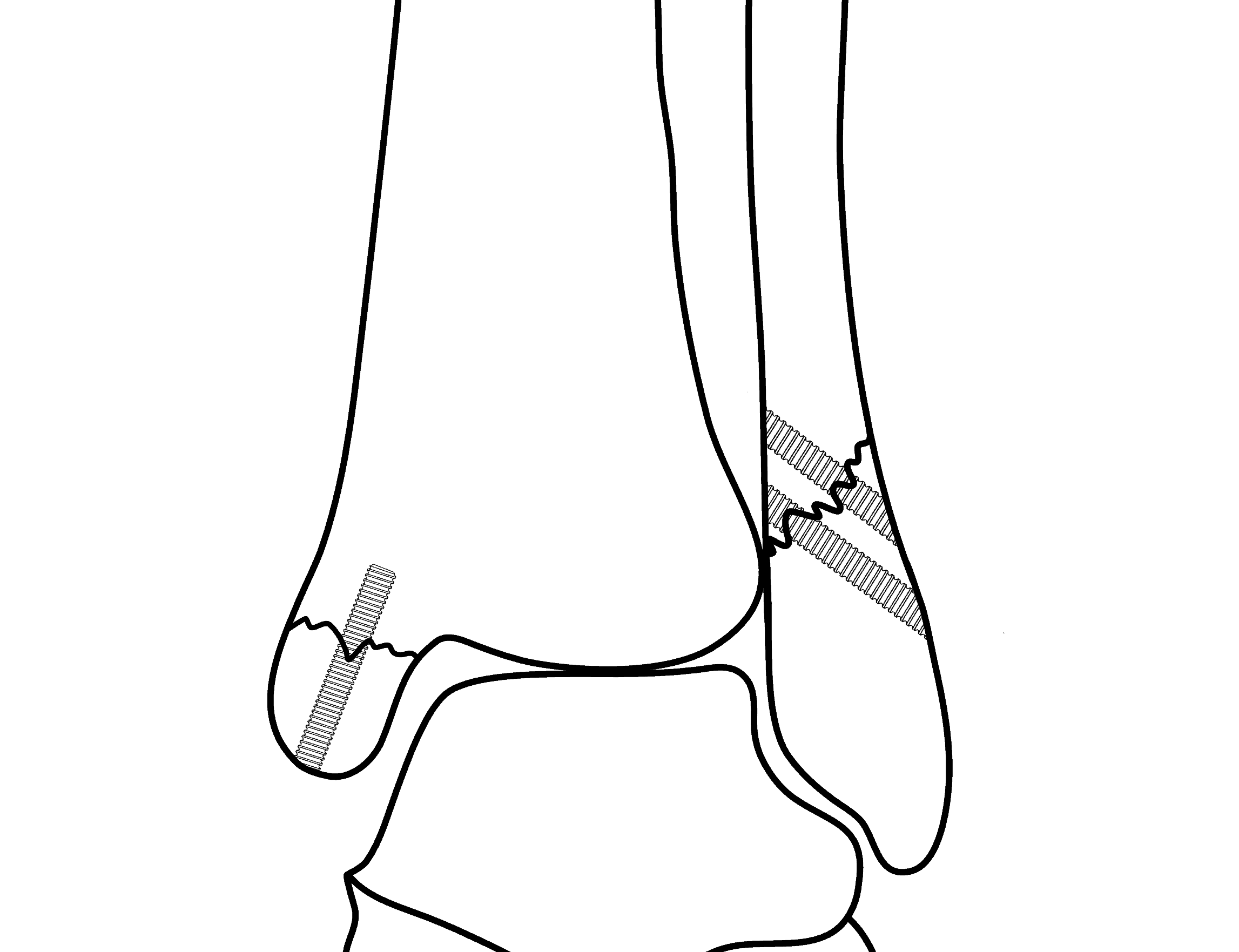
Bimalleolar equivalent fracture
It is called a bimalleolar equivalent fracture when only one bone is broken but the ligaments on the inner part of the bone are injured. This torn ligament may cause the talus to shift and the ankle to slip. Surgery is necessary.
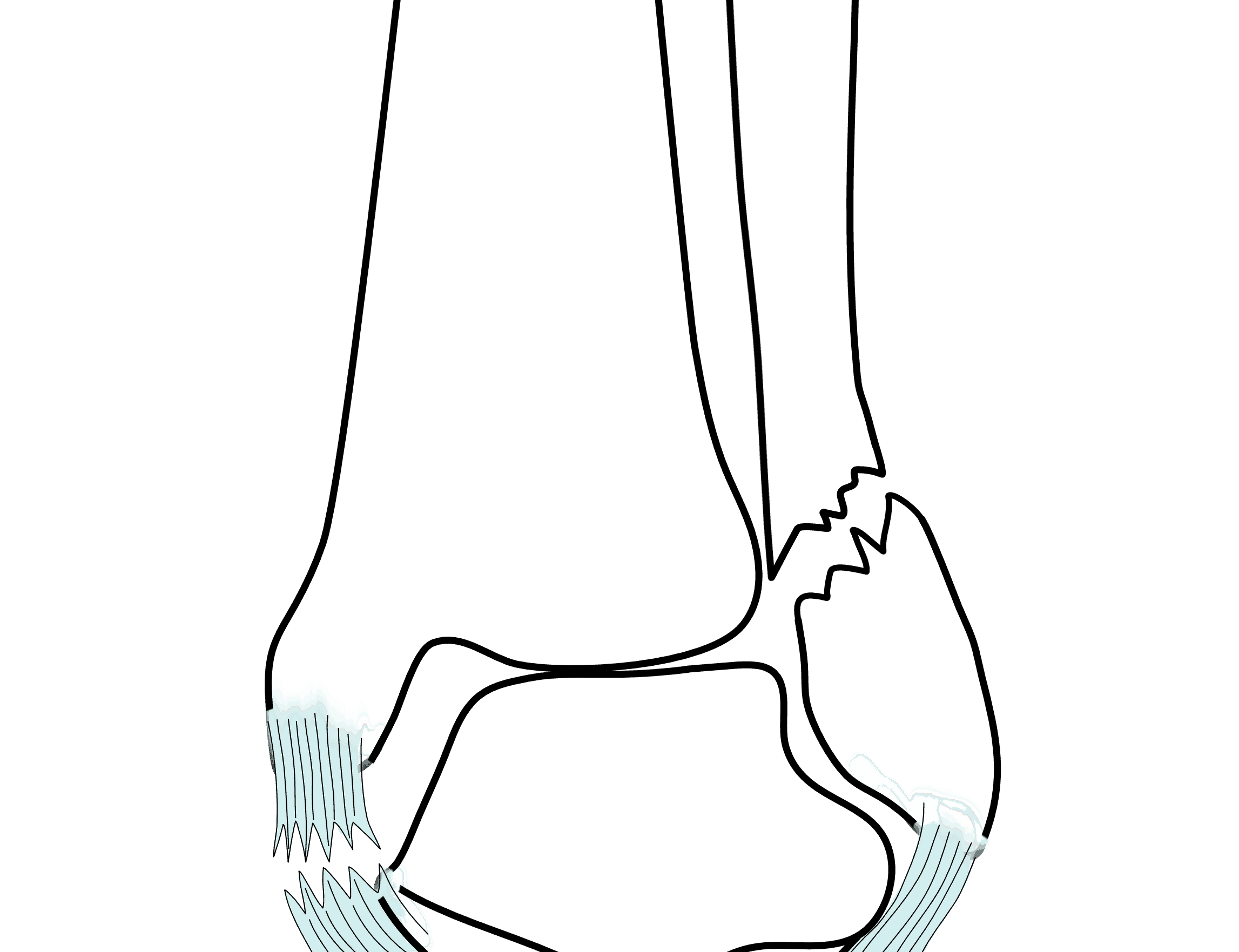
Trimalleolar ankle fracture
In trimalleolar ankle fracture, all 3 bones of the ankle joint are broken, making them extremely unstable. Surgery is necessary.
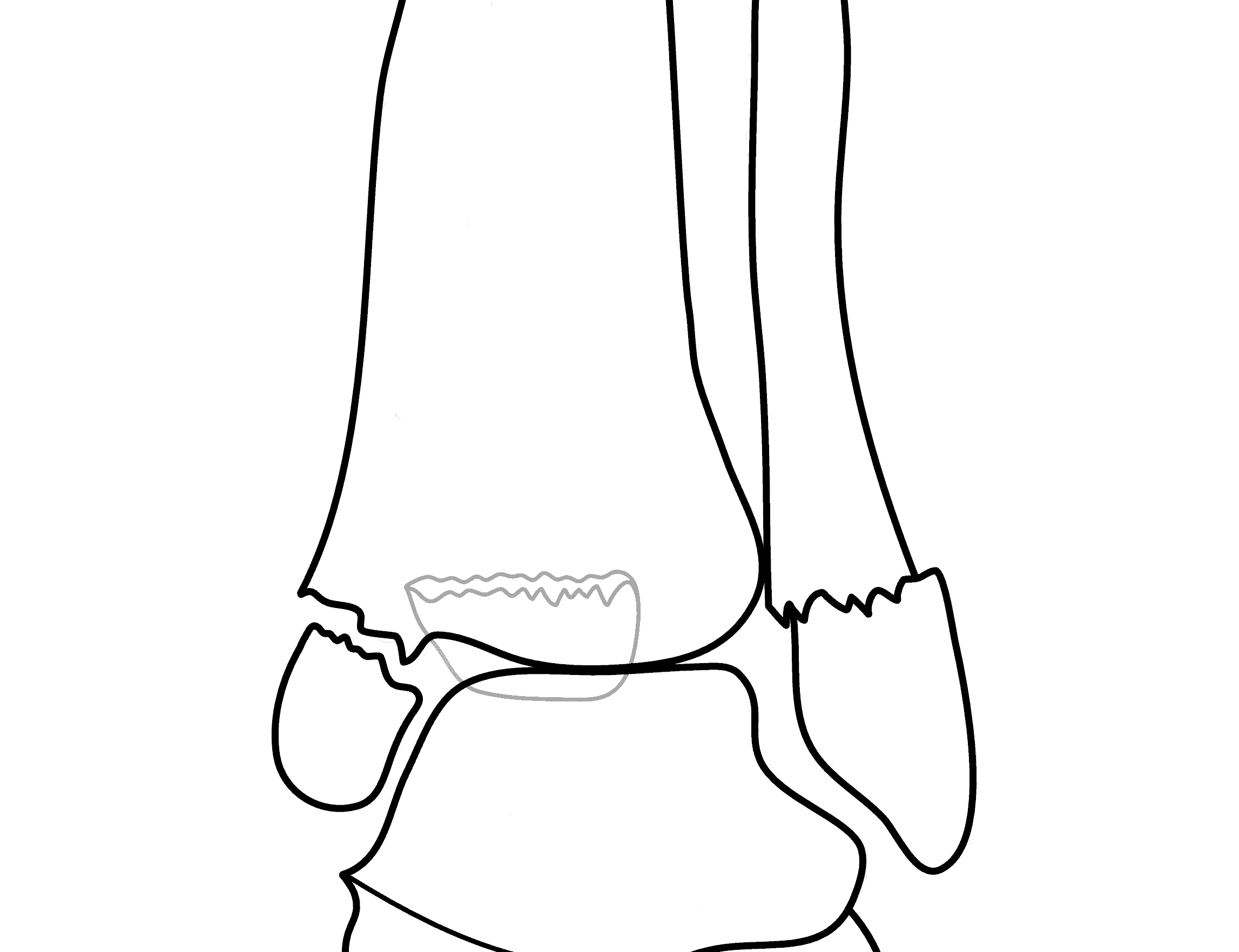
Syndesmosis injury
Syndesmosis is a group of ligaments that stabilize the ankle joint. If the syndesmosis injury affects only the ligaments, it is often referred to as a sprain and can be treated conservatively in most cases. If, in addition to the torn ligament, bones of the ankle joint are also broken, surgery is necessary.
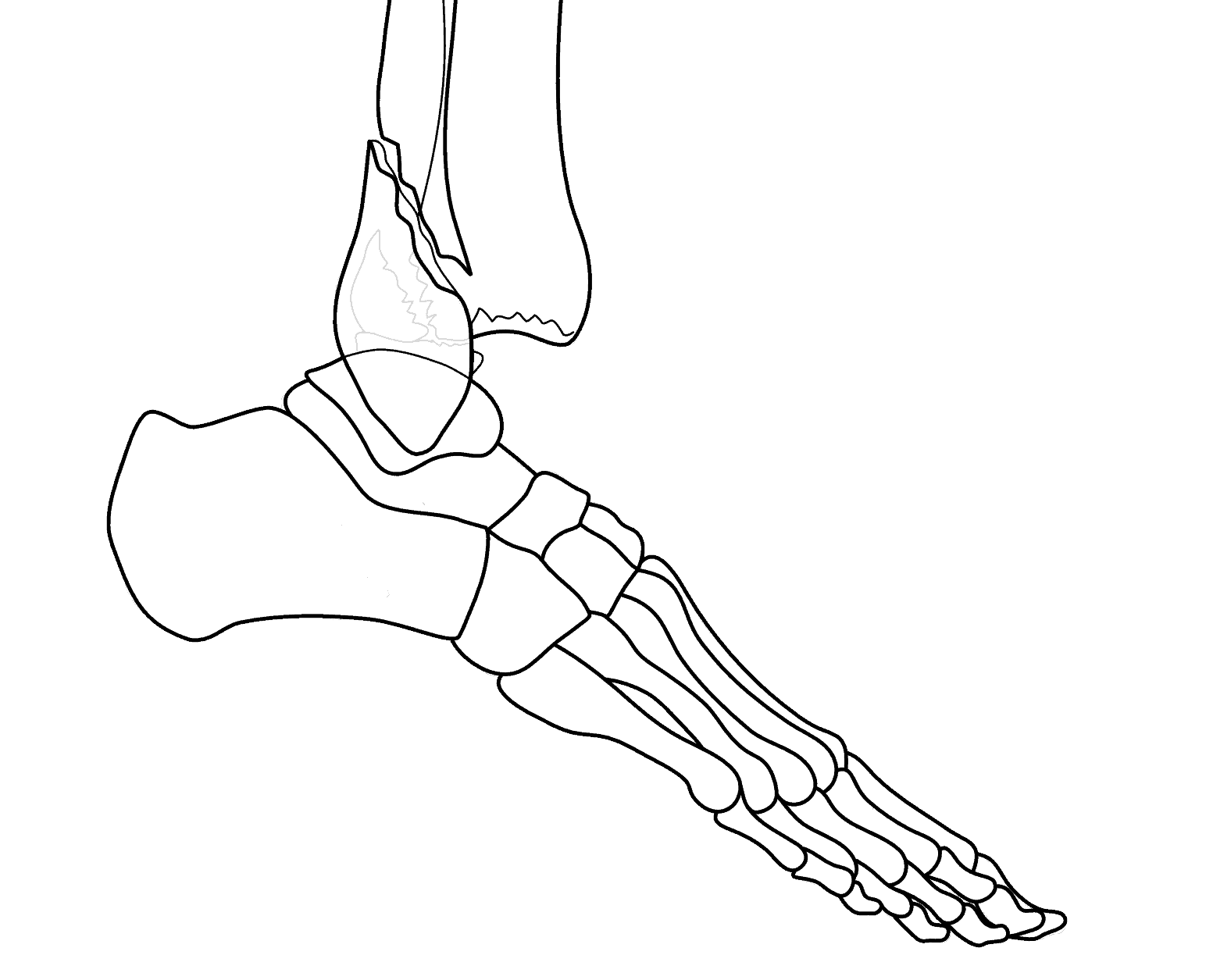
The pilon tibial fracture
In medicine, the “tibial pilon” is basically the joint-bearing part of the tibia (shinbone = tibia). Thus, pilon tibial fracture is a severe form of ankle fracture and is often the result of accidents. A pilon fracture can usually only be treated satisfactorily by surgery. During such an operation, screws made of human bone and / or plate made of metal are used.
Maisonneuve
The Maisonneuve fracture is also a special type of ankle fracture and is classified as a Weber C fracture. The fracture in a Maisonneuve fracture is above the syndesmosis (ligamentous structure). Therefore, the ligament structure is usually additionally injured. Surgery is necessary in most cases.
Treatment options for fractures in the ankle joint
The respective treatment depends on the type of fracture, i.e. it has to be distinguished whether the fractured ankle joint is open or closed, displaced or not displaced. Whether conservative or surgical, the goal of both treatment methods is to heal the fracture.
Surgical techniques of ankle fracture
There are many different surgical techniques that can be performed for an ankle fracture. A distinction is made between arthroscopic procedures, minimally invasive procedures, open surgery and joint-preserving surgery.
Operatively treat broken ankle joint
If conservative therapy is not possible, the broken ankle must be operated on. Here, depending on the type of fracture, screws made of bone are used. Surgery by an ankle fracture specialist is recommended to best rule out post-traumatic osteoarthritis. This is only possible if the joint situation before the accident is restored as best as possible.
Heal broken ankle without surgery
Ankle fractures can often be treated without surgery, but this requires a stable and non-displaced ankle fracture. If the fracture is open or displaced, surgery is usually always performed.
In conservative treatment (without surgery) of a broken ankle, the foot is immobilized until the swelling has subsided. For this, the patient receives a split lower leg cast. Once the swelling has subsided, the lower leg cast is replaced by a circular cast, a special orthosis or a plastic splint. The foot should be immobilized for about 6 weeks. Throughout this time, care should be taken to ensure appropriate thrombosis care, as immobilizing the foot can cause blood clots. It is essential to ensure correct anatomical alignment, as even slight irregularities lead to post-traumatic joint wear (osteoarthritis). If the foot cannot be aligned correctly surgery is necessary -.> More about this in the next chapter
Surgical techniques of ankle fracture
Material | Vorteile | Risiken |
Shark Screw® | Integration in Knochenumbauprozess | Keine Metallentfernung | 100 % biologisch | Geringe Schmerzen nach der Operation | 1-4 Wochen nach der Operation besondere Vorsicht bei der Belastung des Fußes |
Schrauben aus Metall | Bei vielen Operationen einsetzbar | Metallentfernung möglich | Einsatz bei Allergikern & Wetterfühligkeit vermeiden |
Metallplatte | Hohe Festigkeit und Stabilität | Metallentfernung wahrscheinlich |
Shark Screw®- the screw made from human bone
The Shark Screw® is a screw made from human donor bone. It is used for various ankle fractures. The great advantage of the Shark Screw is that the screw is colonized by the body’s own cells after insertion. This happens because of the so-called Havers channels inside the screw. Bone cells and the body’s own vessels can settle in these channels.. Shark Screw® Surgeons enable their patients with Shark Screw® eine 100% biologische Osteosynthese.
Aftercare of the ankle fracture
After surgical treatment of an ankle fracture, the first priority is rehabilitation. Physiotherapy and intensive training must be used to restore the mobility and coordination of the ankle. Always follow the instructions of your treating doctor or health care professional.
Late effects of ankle fracture
Pain, malalignment, incorrect healing of the fracture (joint unevenness) and instability after a fracture should always be examined by an expert. The following late effects can occur after an ankle fracture:
- Soft tissue damage & shortening
- Posttraumatic arthrosis of the ankle joint
- Bone-cartilage damage (osteochondral lesions)
- Pseudarthrosis (unhealed bone)
- Syndesmosis damage & ligament damage
- Steps & deformity (in the joint surfaces)
Ankle joint arthrosis / post-traumatic ankle joint arthrosis
Osteoarthritis is an irreversible damage of the cartilage. In addition, the respective bone may also be affected. If the osteoarthritis occurs a few years after an ankle fracture, it is also called post-traumatic ankle osteoarthritis. “This arthritis occurs when the joint surfaces in the fractured ankle cannot be perfectly reduced. The cartilage surfaces no longer slide properly and rapid joint wear occurs. Therefore, it is very important to be operated by a proven expert,” says Dr. Boris Tirala, who also counts severe ankle injuries among his specialties. The symptoms of ankle arthritis depend on the stage. In early stages, osteoarthritis provides little pain, but if it progresses, deep-seated pain as well as a pulling sensation in the joint are signs of it. To get the pain under control, usually only an arthrodesis (stiffening) of the affected ankle joint helps.
FAQ:
Wird nach einem Bruch des Sprunggelenks zu früh belastet, kann diese die Wundheilung hinauszögern sowie zu einer Refraktur führen. Befolgen Sie unbedingt die Behandlungsempfehlung Ihres Chirurgen oder ihrer Chirurgin! Nach einer Sprunggelenksfraktur sollte man frühestens nach 6 Monaten mit langsamem Joggen anfangen. Belastet man die Fraktur zu früh, besteht die Gefahr der Bildung einer Pseudarthrose. Das Steuern eines Fahrzeuges ist erst dann wieder gewährleistet, wenn das Sprunggelenk wieder schmerzfrei belastet werden kann. Zusätzlich muss die Koordination vollständig gegeben sein.
Grundsätzlich können nur Brüche bei denen die Syndesmose sowie das Sprunggelenk intakt sind ohne Operation behandelt werden können. Die Ruhigstellung dauert dabei 6 – 8 Wochen, kann aber je nach Patienten oder Patientin variieren.
Dies ist von Patienten zu Patienten unterschiedlich. In der Regel sollte das Sprunggelenk 6 Wochen lang nicht belastet werden. Danach kann mit dem Wiederaufbau von Koordination und Muskulatur begonnen werden. Es dauert in etwa 3-6 Monate, bis die normale Belastbarkeit des Sprunggelenks hergestellt. Die Dauer der Krankschreibung ist abhängig vom Beruf des jeweils betroffenen Patienten oder der Patientin.

The author - FA Dr. Boris Tirala
Dr. Boris Tirala is a specialist in orthopedics and trauma surgery at the Schwaz District Hospital in Tyrol. He is also an expert in hallux valgus surgery, hallux rigidus, flatfoot surgery and osteoarthritis.

